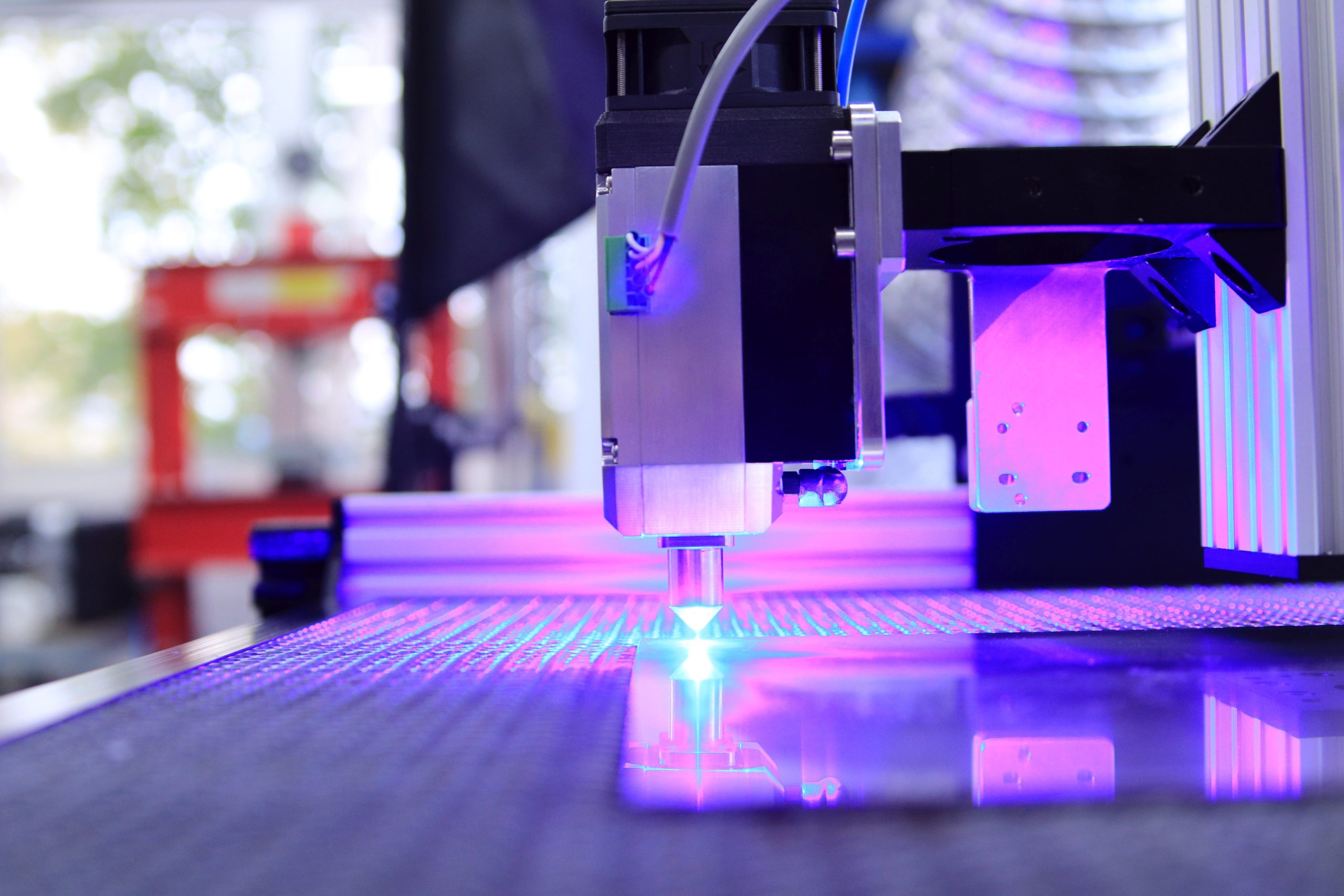
Laser engraving machines have revolutionized the field of engraving, providing precision, versatility, and efficiency that traditional methods struggle to match. These machines utilize laser technology to etch or mark various materials with intricate designs, text, or images. In this article, we will delve into the types of laser engraving machines and explore the numerous benefits they offer.
Basic Components of a Laser Engraving Machine:
Laser Source:
The heart of a laser engraving machine is the laser source. Common types include CO2 lasers, fiber lasers, and diode lasers. Each type has specific properties and is suitable for different materials.
Control System:
Laser engraving machines are equipped with a control system that manages the movement of the laser beam. This system interprets the digital design or pattern, directing the laser to follow the desired path with precision.
X-Y Motion System:
To achieve accurate engraving, laser machines employ an X-Y motion system. This system consists of motors and mirrors that move the laser head along the X and Y axes. The combination of these movements allows the laser to cover the entire engraving area.
Laser Head:
The laser head is the component responsible for focusing and directing the laser beam onto the material’s surface. It often contains a lens that helps concentrate the laser into a fine point for detailed engraving.
How Laser Engraving Works:
Digital Design Input:
The process begins with a digital design or pattern that the user wants to engrave. This design is typically created using graphic design software and then converted into a format compatible with the laser engraving machine.
Material Preparation:
The material to be engraved is placed on the engraving bed. Depending on the material type, the machine may require specific preparation steps, such as applying a coating or using a certain type of engraving surface.
Laser Setup:
The operator sets the parameters for the laser engraving, including power, speed, and frequency. These settings vary based on the material being engraved and the desired depth of the engraving.
Laser Emission:
Once the setup is complete, the laser source emits a concentrated beam of light. In CO2 lasers, this beam is typically invisible, while in fiber and diode lasers, the beam may be visible.
Engraving Process:
The laser head, guided by the control system, moves along the X and Y axes, directing the laser beam onto the material’s surface. The energy from the laser beam interacts with the material, causing it to vaporize, melt, or change color, depending on the material type.
Cooling and Ventilation:
As the laser interacts with the material, heat is generated. Laser engraving machines are equipped with cooling and ventilation systems to dissipate this heat and prevent damage to the machine and the material.
3 Major Types of Laser Engraving Machines:
CO2 Laser Engraving Machines:
These machines use a carbon dioxide gas laser to produce a focused beam of light. CO2 lasers are highly effective for engraving on materials like wood, acrylic, glass, leather, and certain plastics. They are particularly popular for artistic and decorative applications.
Fiber Laser Engraving Machines:
Fiber lasers utilize optical fibers doped with rare-earth elements to generate a laser beam. These machines excel in engraving metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, and brass. They are widely used in industries such as jewelry making, metal fabrication, and electronics.
Diode Laser Engraving Machines:
Diode lasers are solid-state lasers that use diodes as the laser source. While not as powerful as CO2 or fiber lasers, they are suitable for engraving on materials like wood, leather, and certain plastics. Diode laser engraving machines are known for their compact size and energy efficiency.
Major Applications Of Laser Engraving Machines
Laser engraving machines find widespread applications across various industries and creative fields due to their precision, versatility, and efficiency. Here are some key applications of laser engraving machines:
1. Industrial Marking and Etching:
Materials: Metals, plastics, ceramics
Use Cases: Laser engraving machines are extensively used for marking and etching serial numbers, logos, and other identification information on industrial components. This is common in aerospace, automotive, and electronics manufacturing.
2. Personalized Products and Gifts:
Materials: Wood, glass, acrylic, leather
Use Cases: Laser engraving enables the customization of products such as wooden plaques, glass awards, leather accessories, and personalized gifts. It adds a unique and sentimental touch to items, making them ideal for special occasions.
3. Jewelry and Watchmaking:
Materials: Precious metals (gold, silver), gemstones
Use Cases: Laser engraving machines are employed for intricate engraving on jewelry items and watch components. This includes adding serial numbers, brand logos, or intricate designs without compromising the delicate nature of these pieces.
4. Medical Instruments and Devices:
Materials: Stainless steel, plastics
Use Cases: Laser engraving ensures precise marking on medical instruments and devices, facilitating identification, traceability, and compliance with regulatory requirements. It is crucial for maintaining hygiene standards in the medical field.
5. Architectural Signage and Branding:
Materials: Metal, acrylic, wood
Use Cases: Laser engraving can create architectural signage, company logos, and branding elements. It provides a professional and durable solution for outdoor and indoor signage in commercial spaces.
6. Electronics and IT Components:
Materials: Plastic, metal
Use Cases: Laser engraving is used for marking serial numbers, barcodes, and branding on electronic and IT components. It ensures traceability, assists in quality control, and enhances the aesthetic appeal of electronic devices.
7. Art and Decorative Items:
Materials: Wood, glass, acrylic, paper
Use Cases: Artists and designers use laser engraving machines to create intricate patterns, art pieces, and decorative items. This technology allows for detailed and precise designs that might be challenging to achieve through traditional methods.
8. Textile and Apparel Industry:
Materials: Fabric, leather
Use Cases: Laser engraving is also in the textile and apparel industry for creating customized designs on fabrics and leather products. This includes patterns on clothing, accessories, and footwear.
9. Promotional Products:
Materials: Various materials
Use Cases: Laser engraving machines are ideal for personalizing promotional products such as pens, keychains, and USB drives. This adds value to promotional items and enhances brand visibility.
10. Model Making and Prototyping:
Laser engraving machines are also common in model making and prototyping to create detailed prototypes, architectural models, and product prototypes with precision and speed.
Benefits of Laser Engraving Machines:
Precision and Detail:
Laser engraving provides unparalleled precision, allowing for the creation of intricate designs and detailed patterns. This level of accuracy is challenging to achieve with traditional engraving methods.
Versatility in Materials:
Laser engraving machines can work on a diverse range of materials, including wood, metal, glass, acrylic, leather, and more. This versatility makes them valuable tools for various industries and applications.
Speed and Efficiency:
Laser engraving is a swift process, unlike traditional methods. The laser beam moves rapidly across the material, resulting in faster production times. This efficiency is especially crucial for businesses and manufacturers with high-volume demands.
Customization and Personalization:
One of the key advantages of laser engraving is the ability to customize products. Whether it’s adding personalized messages, logos, or intricate designs, laser engraving allows for a high degree of customization, making products unique and special.
Non-contact Process:
Laser engraving is a non-contact process, meaning the engraving tool does not physically touch the material. This eliminates the risk of damage or distortion, ensuring a clean and precise outcome.
Conclusion:
Laser engraving machines have transformed the world of engraving with their speed, precision, and versatility. They have become indispensable in various fields. Over the years, China has become one of the biggest suppliers of laser engraving machines. This is mainly because of the high quality and affordability that Chinese manufacturers are offering.